Several causes of infertility can be treated with intrauterine insemination (IUI), a fertility treatment that closely resembles natural conception. The basic principle of IUI involves injecting specially prepared sperm directly into the uterus at the time of ovulation.
For further information or Booking..
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment procedure in which specially prepared sperm are injected directly into the uterus. IUI is commonly recommended for couples who experience difficulty conceiving due to various factors, including:
-
Women with irregular ovulation
-
Men with mild abnormalities in sperm quality
IUI may also be suitable for couples who face challenges related to timing or are unable to have regular sexual intercourse. In addition, it is frequently recommended for couples with unexplained infertility, in which no specific cause of infertility can be identified.
Studies have shown that among couples with unexplained infertility—particularly when the woman is over 35 years of age and has been trying to conceive for at least two years, and when the male partner has normal sperm parameters—the chance of pregnancy with IUI is approximately 8–12% per cycle. Most pregnancies typically occur within the first three IUI cycles, with a significant decline in success rates after the fourth cycle. In such cases, in vitro fertilization (IVF) offers a higher pregnancy success rate, exceeding 50% per embryo transfer.
Limitations of IUI
IUI may not be appropriate in the following situations:
-
Women over 40 years of age, those with diminished ovarian reserve, or those with irregular or absent menstrual cycles
-
Blocked or severely damaged fallopian tubes due to adhesions
-
Severe male factor infertility, including very low sperm count or poor sperm motility
-
Advanced pelvic endometriosis with significant adhesions
Factors Influencing IUI Success
Several key factors influence the success rate of IUI, including:
-
Woman’s age (younger age is associated with higher pregnancy rates)
-
Number of sperm used during insemination (a higher sperm count—ideally more than 5 million motile sperm—improves success rates)
-
Type of ovulation induction medication (certain medications are associated with better outcomes)
IUI Treatment Process
The IUI treatment process typically begins with ovarian stimulation. Medications to stimulate follicle (egg) development are usually started on the second or third day of the menstrual cycle, with the first day of menstruation counted as day one. These medications are generally taken for approximately 8–10 days.
Around day 12 of the menstrual cycle, a transvaginal ultrasound examination is performed to assess follicle growth and measure follicular size. When the leading follicle reaches approximately 18–20 mm in diameter, a medication is administered to trigger ovulation. The insemination procedure is then scheduled 36–40 hours later.
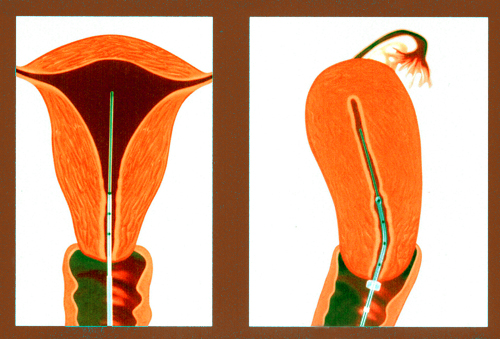
The insemination procedure itself is simple and comparable to a routine pelvic examination. It does not require hospitalization, and patients can return home immediately afterward. On the day of insemination, the male partner provides a semen sample at the clinic, which is collected through masturbation into a sterile container.
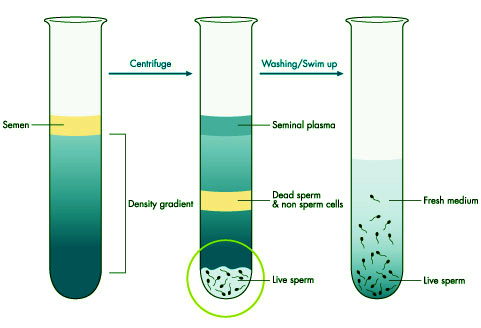
The semen sample is processed in the laboratory to separate and concentrate healthy, motile sperm. These prepared sperm are then injected directly into the uterus using a thin catheter.
Video demonstrating the intrauterine insemination (IUI) technique.
How Many Times Should IUI Be Performed, and When Should Treatment Options Change?
In general, IUI should not be performed more than three cycles. If pregnancy does not occur after three attempts, alternative fertility treatments should be considered.
For women aged 35 years and older, it is usually recommended to limit IUI to a maximum of two cycles, as fertility naturally declines with age. In such cases, alternative treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may offer higher success rates.
How Many Sperm Cells Are Needed for a Successful Pregnancy?
For IUI to be effective, the recommended sperm count is at least 5 million motile sperm per insemination. If the number of motile sperm after laboratory preparation is below this threshold, the likelihood of pregnancy is significantly reduced. In these situations, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) should be considered as an alternative treatment.
Does Performing IUI Once or Twice per Cycle Improve Pregnancy Chances?
Performing insemination once or twice per cycle does not significantly affect pregnancy outcomes. The most critical factor is accurate timing of ovulation. When ovulation timing is precise, a single insemination per cycle is usually sufficient.
Accurate ovulation timing is achieved through the use of ovulation-stimulating medications, medications to prevent premature ovulation, and careful monitoring using blood or urine tests to confirm the optimal timing for insemination.
Possible Reasons for Unsuccessful IUI
Several factors may contribute to unsuccessful IUI, including:
-
Poor egg quality
-
Poor sperm quality or very low sperm count
-
Sperm abnormalities that prevent fertilization
-
Blockages or abnormalities in the fallopian tubes that interfere with egg and sperm interaction
-
Structural abnormalities that prevent the egg from entering or traveling through the fallopian tubes
Recommendations After IUI Treatment
Because IUI closely resembles natural conception, post-procedure recommendations are generally similar to those following natural intercourse.
-
There are no specific restrictions on daily activities; normal exercise and sexual intercourse are allowed.
-
Mild lower abdominal discomfort after insemination is common and is usually caused by ovulation or mild uterine contractions triggered by the procedure.
-
Some women may experience slight spotting or breast tenderness.
-
Vaginal hormonal supplementation may be prescribed to support hormone levels during ovulation stimulation. If ovulation induction is achieved with oral medications alone, additional vaginal supplementation may not be necessary.
-
Pregnancy testing can typically be performed 12–14 days after insemination.
Additional Information on IUI Success Rates
The pregnancy success rate of IUI is approximately 10–20% per cycle. Because IUI is considered a semi-natural fertility treatment, its success rate is moderate.
If pregnancy does not occur after 2–3 IUI cycles (depending on the woman’s age), IVF is generally recommended as the next step. IVF typically offers higher success rates—approximately 50% or more per embryo transfer, particularly in women under the age of 35.