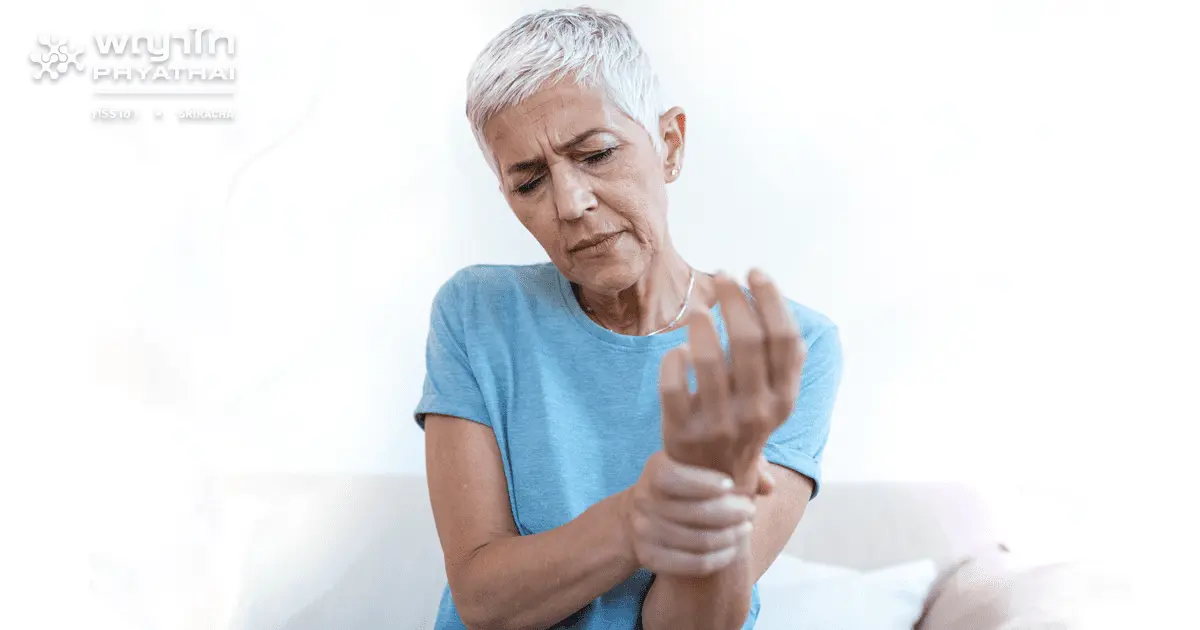
The older you are, the higher your risk of developing joint degeneration.
For further information or Booking..
It may sound frightening, but joint degeneration is a condition that affects many older adults—and some may not even show symptoms despite having the disease. This lack of symptoms can delay treatment and worsen the severity of the condition.
The risk of joint degeneration increases with age. It is classified as an inflammatory joint disease involving the gradual deterioration of the cartilage that covers the ends of the bones. It can occur in both men and women, and there are five high-risk groups, including:
-
Individuals aged 50 and above who frequently engage in heavy physical labor or strenuous activities
-
Individuals aged 70 and above, accounting for 80–90% of cases
-
Overweight individuals, as excess body weight increases stress on weight-bearing joints, especially the knees and hips
-
People with poor joint habits, such as sitting cross-legged, prolonged squatting, or frequent kneeling
-
Individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, joint infections, or previous joint injuries that damage cartilage and accelerate joint degeneration
If you experience persistent pain or stiffness during movement, it is advisable to consult a physician promptly.
Recognizable Symptoms of Joint Degeneration
-
Cracking or popping sounds during joint movement
These may result from bone spurs forming as the body attempts to stabilize the affected joint. -
Pain during movement
Caused by friction between deteriorated joint surfaces. Over time, avoiding movement due to pain may lead to muscle weakness. -
Morning stiffness
Difficulty moving joints or discomfort upon waking. -
Leg deformities
Such as bow-leggedness, outward rotation, or limited extension of the joint.
Diagnosing Joint Degeneration
To determine the severity of the condition, physicians may use:
-
A physical examination to evaluate joint movement and skeletal alignment
-
X-rays or MRI scans of the affected joints
-
Bone Mass Densitometry (BMD) to measure bone density
6 Treatment Approaches for Improving Quality of Life in the Elderly
1. Physical Therapy
Used to relieve muscle stiffness, increase flexibility, and reduce pain. The physician will determine the appropriate therapy based on the patient’s condition.
2. Medications
Anti-inflammatory drugs or pain relievers may be prescribed to ease discomfort and help patients resume daily activities.
3. Joint Lubrication Injections
Such as artificial joint fluid (viscosupplementation) to improve joint lubrication and reduce pain.
4. Arthroscopic Debridement
A minimally invasive procedure that allows the doctor to clean the joint, smooth damaged surfaces, or repair injured ligaments or cartilage.
5. Corrective Osteotomy
A surgical procedure to realign a misaligned knee joint, helping redistribute weight and reduce strain on damaged areas.