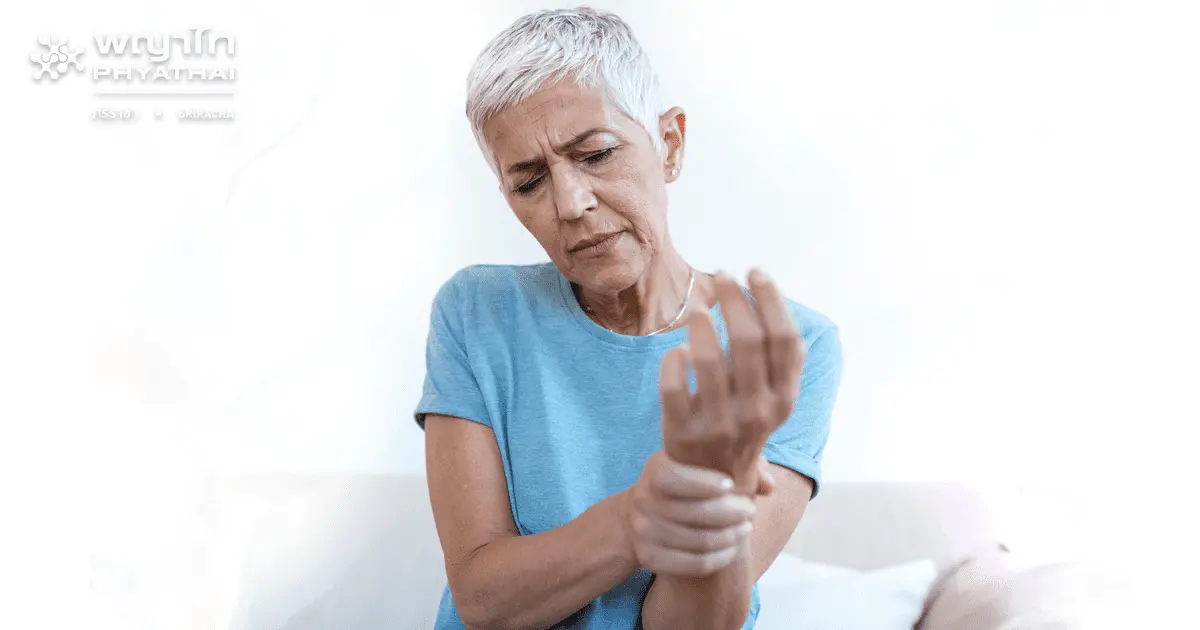
It may sound frightening, but joint degeneration is a condition that poses a risk to all elderly individuals. Some people may not show any symptoms at all, allowing the disease to progress silently and become increasingly severe over time.
For further information or Booking..
The older you are, the higher the risk.
Joint degeneration is a type of inflammatory joint disease involving the gradual breakdown of cartilage that cushions the ends of bones. It can occur in both men and women. The following five groups are particularly at risk:
People at Higher Risk
-
Individuals aged 50 and above who frequently engage in heavy physical activity
-
Individuals aged 70 and above, accounting for 80–90% of cases
-
Overweight individuals, as excess weight increases stress on weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips
-
Individuals with improper joint habits, such as sitting cross-legged, prolonged squatting, or frequent kneeling
-
Individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, joint infections, or joint injuries that damage cartilage and accelerate degeneration
If you experience persistent pain or stiffness, see a doctor promptly.
Common Symptoms of Joint Degeneration
-
Crackling sounds during movement; some may also develop bone spurs, formed as the body attempts to stabilize the joint
-
Pain during movement due to bone-on-bone contact; prolonged pain may cause reduced joint movement and muscle weakness
-
Morning stiffness or discomfort after waking up
-
Leg deformities, such as bow-legged appearance or outward rotation, with limited joint extension
How Doctors Diagnose Joint Degeneration
-
Physical examination and musculoskeletal assessment by an orthopedic specialist
-
X-ray or MRI imaging to evaluate affected joints
-
Bone density measurement using Bone Mass Densitometry (BMD)
6 Treatment Approaches to Improve Quality of Life in Older Adults
1. Physical Therapy
Helps reduce muscle stiffness, improve joint mobility, and relieve pain. Physicians will recommend appropriate rehabilitation techniques.
2. Medications
Anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving drugs help reduce symptoms and allow patients to resume normal daily activities.
3. Joint Lubrication or Viscosupplementation
Injections of lubricating substances or artificial joint fluid help reduce friction and ease pain.
4. Arthroscopic Debridement
A minimally invasive surgery used to diagnose and clean the joint, reshape damaged surfaces, or repair torn ligaments or cartilage.
5. Corrective Osteotomy
A procedure that realigns the knee joint to improve weight distribution and reduce stress on damaged areas.
6. Joint Replacement Surgery
Recommended when medications and physical therapy no longer provide relief.
This surgery replaces damaged joint surfaces with materials such as cobalt alloy and specialized polyethylene, which mimic natural joint function and are safe for surrounding tissues. It helps patients regain mobility and significantly reduces pain.
If your elderly loved ones are experiencing joint problems, you can consult a joint rehabilitation specialist at the Orthopedic and Joint Disease Center, Phayathai Sriracha Hospital.
For further information or Booking..