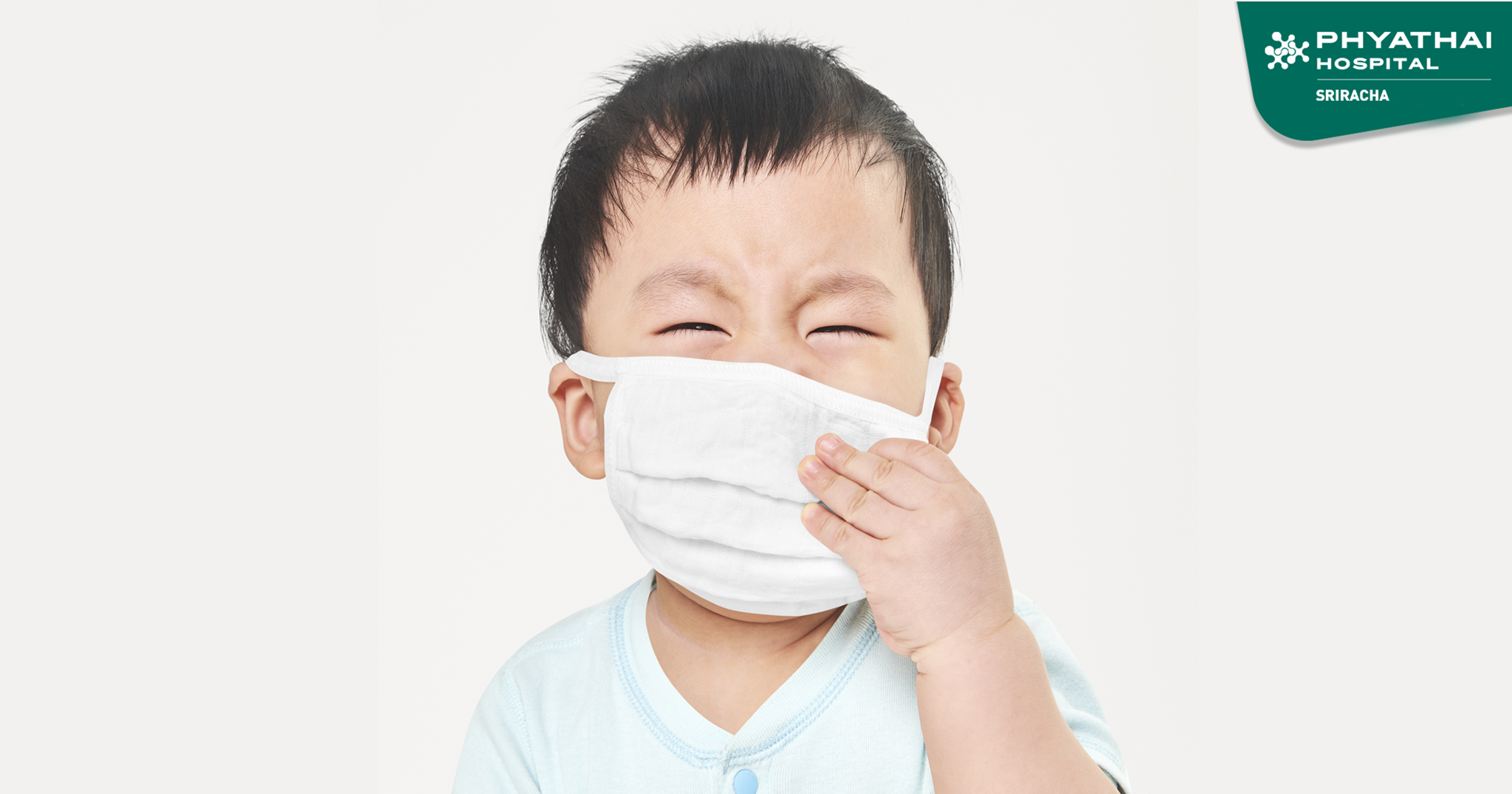
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a common contagious illness that primarily affects children under the age of five, particularly during the rainy season. It is caused by several strains of viruses belonging to the Enterovirus group. While most cases are mild and self-limiting, infection with the Enterovirus 71 (EV71) strain can lead to serious complications, including encephalitis, which may be life-threatening.
For further information or Booking..
How Does Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Spread?
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) can spread through both direct and indirect contact. Direct transmission occurs through contact with the nasal secretions, saliva, or feces of an infected person. Indirect transmission can occur through contact with contaminated objects such as toys, utensils, water, or food.
HFMD commonly spreads in kindergartens and childcare centers because the virus has an incubation period of approximately one week, during which infected individuals may transmit the virus before symptoms become apparent.
What Are the Symptoms of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
Common symptoms include fever, mouth pain or sore mouth, excessive drooling, and decreased appetite due to painful mouth sores. A rash consisting of red spots or fluid-filled blisters may appear on the hands, feet, buttocks, genital area, and occasionally on the torso.
Symptoms usually improve within about one week. However, dehydration may occur if a child refuses to eat or drink because of mouth pain. In cases caused by the EV71 strain, more severe complications may develop, including encephalitis, breathing difficulties, and seizures, which can be life-threatening.
Treatment and Prevention
There is no specific antiviral treatment for HFMD. Management focuses on symptom relief, including the use of fever reducers, pain relievers, topical anesthetics for mouth ulcers, and oral rehydration solutions to prevent dehydration.
A vaccine is available that provides up to 97% protection against the EV71 strain; however, it does not protect against other strains of the virus. Preventive measures include isolating infected individuals, frequent handwashing, thorough cleaning of contaminated objects, ensuring food and water hygiene, and keeping infected children out of school or childcare facilities until they have fully recovered.